Crackmasters
Terminology
Backfill
Backfilling involves the process of replacing soil that was removed during excavation around or against the foundation walls of basements or crawlspaces. This critical step in construction ensures the stability of the foundation and the surrounding earth. Proper backfilling supports structural integrity, facilitates drainage away from the foundation, and helps protect against water ingress.
Black Mold
Black mold, or Stachybotrys chartarum, is a type of mold that thrives in moist, damp environments and can have severe implications for indoor air quality and health. Exposure to mold spores occurs through inhalation, direct skin contact, or ingestion. The presence of mold is often indicative of excessive moisture and poor ventilation. Effective mold prevention hinges on moisture control within indoor environments, as it eliminates the primary condition necessary for mold growth. While many molds can potentially impact health, black mold is particularly notorious for causing respiratory and other health issues in susceptible individuals.
Capillary Action
Capillary action represents a fundamental principle where water is naturally drawn to and absorbed by porous materials upon contact. This phenomenon is particularly relevant to concrete basement floors and walls due to their inherently porous composition. These surfaces act akin to sponges, absorbing water and potentially storing significant volumes — with instances recorded where a basement has absorbed up to 240 gallons of water during a typical rainfall event.
Cinder Block or Concrete Block/Construction Block
Cinder blocks, also known as concrete blocks or construction blocks, are pre-fabricated structural components made from concrete or a mix of concrete and cinders. These blocks are fundamental in the construction of various structural elements, including foundation walls and retaining walls.
Clay Soil
Clay soil is characterized by its composition of very fine particles, primarily silicates of aluminum and/or iron and magnesium. This type of soil presents unique challenges due to its slow water absorption rate and prolonged moisture retention. Wet clay soil becomes heavy and sticky, experiencing significant expansion, while it can shrink and settle upon drying, often forming a hard, crack-prone surface. The distinct properties of clay soil require careful consideration in construction projects.
Cold Joint
A cold joint represents the point where a new concrete pour meets a previously cured section. Ideally, concrete should be poured continuously to avoid the formation of cold joints, as they can become potential weak spots in the structure. Cold joints may compromise the monolithic integrity of concrete installations and can be more susceptible to water infiltration. Mitigating the impact of cold joints involves strategic planning and execution to ensure structural cohesion and waterproofing efficacy.
Dry Well
Efflorescence
Efflorescence is characterized by a white, crystalline, or powdery deposit that appears on the surfaces of masonry materials, including concrete, brick, and clay tiles. This condition is caused by the migration of water through these materials, which dissolves and transports soluble salts to the surface. Upon the water’s evaporation, these salts are left behind, forming the visible efflorescence.
Erosion
Erosion refers to the process by which land or soil is gradually worn away by the natural forces of wind, water, or ice. This phenomenon can lead to significant changes in landscape structure, affecting soil stability and building foundations.
Excavation
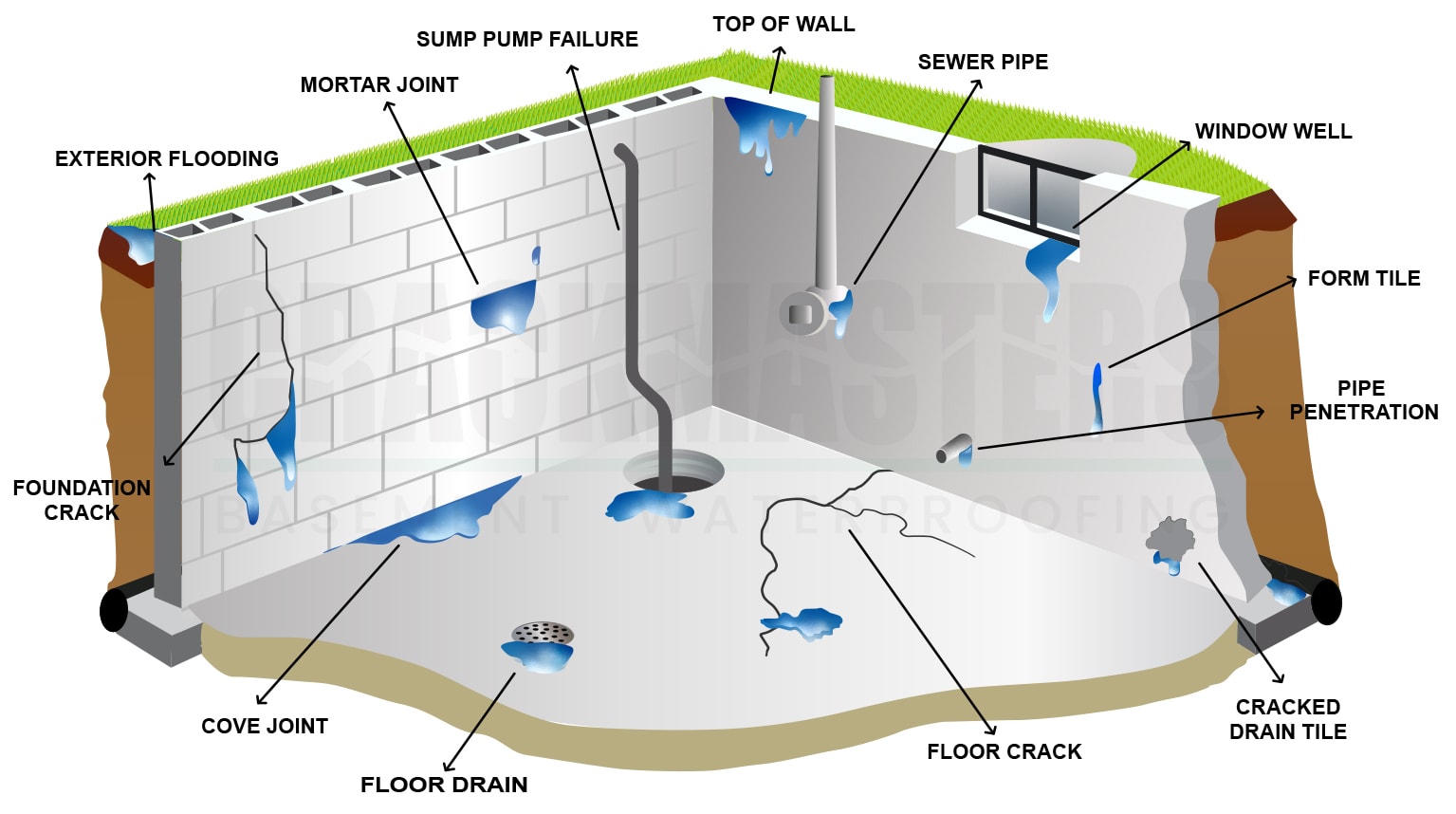
Floor Crack
Foundation
The foundation is the structural base that supports a building or structure, including the base course and footing courses. In the context of a frame house, it encompasses the entire substructure made of masonry or other durable materials. The foundation distributes the weight of the structure evenly across the ground, ensuring stability and resistance to shifting or settling.
Foundation Footings
Footings are the poured concrete bases designed to support foundation walls, columns, or chimneys. They distribute the load of the structure above to the ground below, ensuring stability and preventing settlement. Footings are typically reinforced with steel bars to enhance their load-bearing capacity and resilience against shifting soil conditions.
Foundation Wall
Foundation walls are the critical supporting elements of a structure positioned below the first-floor construction or beneath the ground level. These walls play a pivotal role in transferring the load from the building to the ground, ensuring stability and structural integrity. Foundation walls must be designed and constructed with precision to withstand soil pressure and environmental conditions.
Ground Water
Groundwater refers to the water that permeates through the earth’s surface layers and accumulates above an impermeable rock layer where it cannot, or can only very slowly, continue its downward journey. This natural reservoir is stored in the voids and between the particles of rock and soil.
Hydrostatic Pressure
Hydrostatic pressure occurs as a result of the elevation of the water table, driven by factors such as rainfall, melting snow, or natural springs. This phenomenon leads to a significant increase in pressure beneath the basement floor and against foundation walls. The accumulation of pressure, particularly following substantial rainfall, poses a risk of structural damage to the foundation.
Mildew
Mildew refers to a specific type of mold growth that manifests as a thin, often white or gray, powdery layer on surfaces. It is typically found on living plants or organic materials but can also appear on damp surfaces within buildings. While mildew primarily affects the appearance and surface integrity of the materials it inhabits, it also serves as an indicator of excessive moisture levels that could lead to more serious mold issues.
Mold
Mold encompasses a wide range of parasitic, microscopic fungi, including types like Penicillin, that reproduce through airborne spores. These spores, which float in the air akin to pollen, thrive in moist, poorly ventilated environments such as basements and bathrooms. Mold is not only a concern for structural integrity but also a common allergen that can impact indoor air quality and health.
Mortar Joint
Mortar joints are the seams filled with mortar or grout that secure bricks, blocks, or stones in masonry construction. These joints not only bond the masonry units together, providing structural stability, but also play a crucial role in waterproofing, thermal insulation, and the aesthetic appearance of the structure. The durability and performance of a masonry wall significantly depend on the quality of the mortar joints and their resistance to environmental stresses.
Poured Concrete Foundation
Poured concrete foundations are created by pouring concrete into a set of forms positioned opposite each other, establishing the foundation’s perimeter. This method results in a monolithic, or single-piece, foundation that offers superior strength and integrity. Once the concrete has cured, it provides a solid and continuous barrier against soil pressure and water ingress.
Rust
Rust is the common term for iron oxide, a compound that forms when iron reacts with oxygen and moisture. This chemical reaction results in the characteristic reddish-brown coating that can weaken iron and steel structures over time. Rust is not only a concern for the aesthetic degradation of metal surfaces but also poses significant risks to the structural integrity and longevity of metal components in buildings, vehicles, and infrastructure.
Silt
Silt is a soil substrate characterized by particles that are finer than sand but coarser than clay. Occupying a unique position in the soil texture spectrum, silt particles contribute to the soil’s fertility and water retention capabilities. However, they also pose challenges in terms of stability and drainage.
Sump Pump
A sump pump is an electromechanical device installed in a sump pit, a designated collection area for water entry in the basement. The primary function of a sump pump is to pump out accumulated water, directing it away from the building to prevent water damage and flooding in basements. Sump pumps are a critical component of basement waterproofing systems, ensuring that moisture does not compromise the structural integrity of the foundation or the indoor air quality of the living spaces above.
Tar
Tar is a dark, viscous liquid obtained through the destructive distillation of coal, wood, or other organic materials. Rich in a complex mixture of organic compounds, tar has been utilized for centuries in various applications, most notably in waterproofing and roofing. Its adhesive and water-repellent properties make it an effective sealant for protecting structures from water ingress and damage.
Undermining
Wall Crack
Water Leak
A water leak occurs when water escapes from a system, such as plumbing, roofing, or foundation, through holes, cracks, or other imperfections. Leaks can lead to significant water loss, damage to structures and property, and the potential for mold growth.
Water Seepage
Water seepage describes the movement of water through porous materials or soils, a process also known as percolation. This phenomenon can occur naturally in the environment or within built structures, leading to moisture accumulation in unintended areas such as basements, foundations, and walls.
Water Table
Weeping Tile System or Drain Tile
Weeping tile, or drain tile, is a drainage system consisting of a perforated, corrugated plastic or clay pipe laid at the bottom of the foundation wall. It is designed to channel excess water away from the foundation, preventing groundwater from penetrating the foundation walls. Weeping tiles can direct water to a sump pump, storm drain, or sewer system, playing a crucial role in maintaining a dry and stable foundation. This system, sometimes referred to as a perimeter drain, is essential in areas prone to high groundwater levels or significant rainfall.
CRACKMASTERS BASEMENT WATERPROOFING EXPERTS
KNOW YOUR WET BASEMENT
TERMINOLOGY
Canada’s Trusted Basement Waterproofing Specialists
Foundation Repair & Leaky Basement Concrete Contractors
WET BASEMENT SOLUTIONS




